TMS Vendor Decision Matrix: The 2026 Procurement Framework That Prevents €800K+ Selection Disasters While Navigating AI Hype and ERP Integration Complexity

Last year your procurement process for a TMS vendor might have followed familiar patterns: budget approvals, RFP responses, demo sessions, reference calls. But 2026's TMS vendor selection landscape brings challenges that traditional buyer frameworks weren't built to handle.
ERP providers are reasserting themselves in the TMS space, giving companies more to consider as they evaluate options for 2026, while market consolidation will continue with vendors in adjacent areas like warehouse management or supply chain planning looking to expand into execution, creating new combinations that change the competitive landscape. Meanwhile, procurement teams face mounting pressure to distinguish between genuine AI capability and vendor marketing hype—Gartner warns of widespread 'agent washing' where vendors rebrand existing tools as AI agents.
The stakes are higher than ever. Poor vendor selections in this environment can lead to failed implementations, budget overruns exceeding €800K, and compromised operational efficiency. Your organization needs a decision framework that addresses 2026's unique complexity without falling victim to analysis paralysis.
The 2026 TMS Selection Challenge
Traditional vendor selection matrices fail when confronted with today's TMS marketplace dynamics. Organizations planning major ERP initiatives may want to take another look at the transportation tools that are native to those platforms, which adds an entirely new layer to vendor evaluation. You're no longer just comparing standalone TMS providers like MercuryGate, Descartes, or E2open—you're weighing these against emerging platforms like Cargoson and evaluating whether Oracle or SAP's transportation modules might fit your enterprise architecture strategy.
The AI complexity compounds this challenge. GenAI has been a good tool for surfacing data and helping users get answers faster, but distinguishing genuine AI value from marketing fluff requires specific evaluation criteria. Some TMS providers tout that they're AI when they're probably machine learning at best, while others are building truly differentiated automation capabilities.
The increasing cost of fuel, the decrease in available labor and the constantly changing nature of freight rates have created tremendous pressure on companies to better manage their logistics expenses. TMS platforms provide companies with the ability to optimize their routes, automate carrier selection, conduct freight audit, consolidate loads and plan better, making vendor selection decisions even more consequential for your operational success.
Building Your Decision Matrix Framework
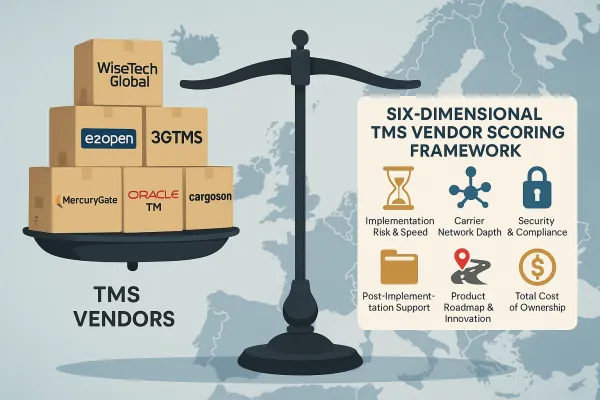
Core Criteria Categories
Your TMS vendor decision matrix must align stakeholder input before scoring begins. Finance cares about total cost of ownership and pricing predictability. Operations focuses on functional fit and user experience. IT emphasizes integration complexity and security. Legal worries about contract terms and compliance requirements.
Structure your evaluation around these core categories:
- Functional criteria: Core TMS capabilities, workflow automation, reporting, and user interface design
- Technical criteria: Integration architecture, scalability, security frameworks, and API maturity
- Commercial criteria: Pricing models, implementation costs, ongoing support fees, and contract terms
- Risk criteria: Vendor financial stability, regulatory compliance, business continuity planning
Each category needs specific, measurable sub-criteria. For functional assessment, don't just ask "Does it handle multi-modal shipping?" Ask "Can it automatically select optimal carrier mix for shipments requiring both ground and air segments?" The specificity forces vendors to demonstrate actual capability rather than checking boxes.
Weighting Your Criteria for 2026 Realities
Your weighted matrix should assign different levels of importance to each criterion, ensuring critical factors reflect procurement priorities. To weight evaluation criteria, ask: 'What would cause this project to fail?' The answers to that (e.g. poor compliance, bad integrations) should be your highest-weighted factors.
Cost management still dominates European procurement priorities heading into 2026. If budget constraints are your primary concern, weight commercial criteria at 35-40%. For organizations undergoing digital transformation, technical integration capability might warrant 45% weighting. Companies in heavily regulated industries should weight compliance and risk criteria at 30% minimum.
Don't make every criterion equally important—that defeats the purpose of a decision matrix. Use a weighting scale where your highest priority areas get 3x-5x the weight of your lowest priority concerns.
AI and Automation Assessment Framework
The AI evaluation component requires its own sub-matrix within your broader framework. In their predictions for the next year, Stanford faculty across computer science, medicine, law, and economics converge on a striking theme: The era of AI evangelism is giving way to an era of AI evaluation. Whether it's standardized benchmarks for legal reasoning, real-time dashboards tracking labor displacement, or clinical frameworks for vetting the flood of medical AI startups, the coming year demands rigor over hype.
Your AI assessment criteria should include:
- Automation depth: Which manual processes can the system actually eliminate versus assist with?
- Decision quality: How does AI-powered carrier selection or routing optimization perform against baseline metrics?
- Learning capability: Can the system improve performance based on your organization's historical data patterns?
- Transparency: Can you audit and understand AI-driven decisions for compliance purposes?
Demand proof, not promises. Ask vendors to demonstrate their AI capabilities using your actual data during evaluation. If they claim AI-powered demand forecasting, run their algorithms against your historical shipping patterns and measure accuracy. If they tout intelligent carrier optimization, compare their recommendations against your current logistics costs.
A credible AI vendor does more than promote cutting-edge research. They connect their technology to enterprise-relevant use cases with measurable outcomes. Executives should expect vendors to explain: Which business functions their models are designed to support, rather than accepting vague AI capability claims.
ERP Integration Complexity Scoring
ERP providers are reasserting themselves in the TMS space, giving companies more to consider as they evaluate options for 2026. Organizations planning major ERP initiatives may want to take another look at the transportation tools that are native to those platforms. This reality demands a dedicated evaluation framework for integration scenarios.
Create separate scoring tracks for different integration approaches:
Native ERP TMS modules: Oracle Transportation Management, SAP Extended Warehouse Management transportation features. Score these on functional gaps compared to standalone solutions, but weight integration simplicity heavily.
Best-of-breed integration: Platforms like Cargoson, MercuryGate, or Descartes connecting to your existing ERP. Focus on API maturity and standardized data flows, since tasks that once required custom development, like connecting a TMS to an ERP system, are easier because of more mature application programming interfaces (APIs).
Hybrid architecture: Some functionality native to ERP, specialized transportation features from dedicated TMS. This requires scoring both technical complexity and operational workflow impact.
For each integration scenario, measure:
- Implementation timeline and resource requirements
- Ongoing maintenance burden and upgrade impact
- Data synchronization reliability and real-time capabilities
- Total cost of integration over five-year period
Vendor Consolidation Risk Assessment
There's still room for more consolidation in the TMS market, and these moves may reshape the options available to shippers, especially as more providers bring planning, execution and visibility tools onto a single platform. Vendors should watch how these changes shape product direction and support models in 2026 as they adjust their offerings to stay competitive.
Your risk assessment framework should evaluate vendor longevity through multiple lenses:
Financial stability: Revenue growth trends, funding runway for private companies, profitability metrics for public vendors. Request financial statements or analyst reports where available.
Market positioning: Whether the vendor is likely acquisition target or acquirer. Small, innovative vendors might deliver superior functionality but face acquisition risk. Large, established players offer stability but may deprioritize transportation features.
Strategic focus: Vendors in adjacent areas like warehouse management or supply chain planning may look to expand into execution. Assess whether transportation is core to the vendor's business model or a secondary product line.
Customer concentration: Vendors overly dependent on few large customers face revenue risk if those relationships change. Look for diversified customer bases across industries and company sizes.
Score each vendor on a 1-5 scale across these stability factors, then weight this component at 15-20% of your total decision matrix. The lowest-risk vendors aren't necessarily the best choices, but you need visibility into the trade-offs.
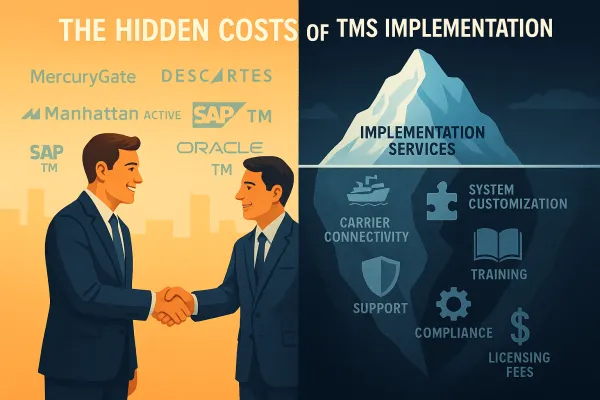
Implementation and ROI Scoring
Implementation success often determines long-term TMS value more than feature functionality. Regular integration implementation varies from 1 to 3 months, but this timeline depends heavily on your internal readiness and vendor support quality.
Your implementation scoring should measure:
Deployment methodology: Does the vendor follow structured implementation frameworks? How do they handle data migration, user training, and go-live support? Request reference customers who went live within the last 12 months.
Resource requirements: What internal team commitment is required during implementation? Can you maintain existing operations while deploying the new system? Score vendors lower if they require extensive internal IT resources you don't have available.
Risk mitigation: How does the vendor handle implementation delays or functionality gaps discovered during deployment? Look for vendors with change order processes and realistic project timelines.
For ROI calculation, focus on measurable outcomes rather than theoretical benefits. Automated systems optimize routing, consolidate shipments, track accessorial trends and identify recurring cost leaks that human teams often overlook. As a result, companies gain more accurate forecasting and stronger rate negotiation power.
Establish baseline metrics before vendor selection: current transportation costs per shipment, manual processing time for common tasks, carrier performance issues. Then score vendors on their ability to deliver specific improvements against these baselines within defined timeframes.
Using Your Matrix for Final Selection
Don't rely solely on the highest numeric score. The matrix helps you understand trade-offs and identify patterns, but requires human judgment for final decisions.
Look for these decision patterns:
Clear winner: One vendor scores significantly higher across multiple categories. This suggests strong alignment between vendor capabilities and your requirements.
Close competition: Top two vendors within 5-10% of each other. Focus on differentiating factors most important to your organization's success.
Specialized strengths: Different vendors excel in different areas. Consider whether you need best-in-class functionality in specific areas or consistent capability across all categories.
Document your scoring methodology and source data. Include vendor quotes, demo feedback, reference call notes, and risk assessment details. This documentation supports procurement decision justification and helps during contract negotiations.
Your decision matrix should also identify your backup vendor. If contract negotiations fail with your first choice, having a clearly defined alternative prevents starting the evaluation process over again.
Remember that European procurement teams have excellent options across the capability spectrum. Whether you choose an established platform like Descartes, an innovative solution like Cargoson, or decide to leverage your ERP provider's transportation module, success depends more on thorough evaluation and proper implementation than on any single vendor's superiority.
The 2026 TMS vendor decision matrix framework prevents expensive selection mistakes by forcing systematic evaluation of complex trade-offs. Use it to navigate AI hype, ERP integration challenges, and consolidation risks while maintaining procurement objectivity throughout your selection process.